Cholelithiasis, known as gallstones, is a very common disease in all countries; in fact, 10% of men and 15% of women in Spain suffer from it.
Cholelithiasis, known as gallstones, is a very common disease in all countries; in fact, 10% of men and 15% of women in Spain suffer from it.
Next, we will talk in depth about gallstones, their types, the complications that can arise and whether or not it is possible to prevent this condition.
In addition, you will have at a glance the signs and signals that may indicate that you need medical attention for possible gall stones.
What are gallstones?
The cholelithiasis or gallstones are hard deposits that form in the gallbladder or bile ducts, a pear-shaped organ located below the liver.
These stones can range in size from tiny grains of sand to larger marble-sized stones.
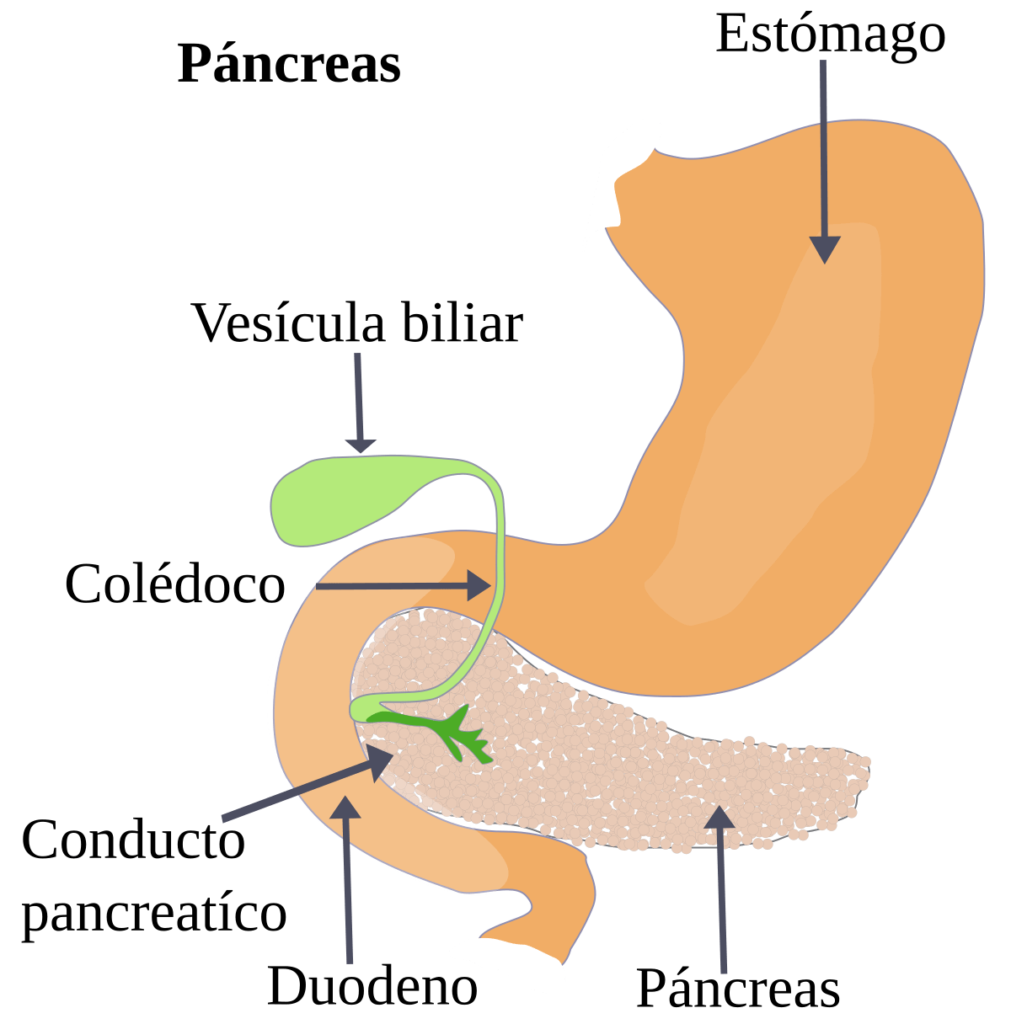
They are composed mainly of cholesterol or bilirubin, two substances found in bile, a fluid produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder.
There are two main types of gallstones.
Cholesterol calculations
These are the most common and are usually composed mainly of cholesterol. They are formed when there is excess cholesterol in the bile.
Bilirubin calculations
Also known as pigment stones, these stones form when there is excess bilirubin in the bile.
They are less common than cholesterol stones.
Signs and symptoms
Gallstones often cause no symptoms and can go unnoticed for years; However, when gallstones cause complications, they can lead to a number of health problems.
The most common symptoms of gallstones include:
- Abdominal pain: The pain usually occurs on the upper right side or in the middle of the abdomen and may be sharp or constant.
- Nausea and vomiting: The presence of gallstones can cause nausea and, in some cases, vomiting.
- Indigestion: Difficulty digesting fatty foods can be a symptom.
- Biliary colic: These are episodes of sudden, severe pain that can occur when a gallstone temporarily blocks the bile duct.
- Jaundice: When a stone blocks the common bile duct, bile can back up into the liver and cause jaundice, which manifests as yellowing of the skin and eyes.
If you experience any of the symptoms above or suspect you may have gallstones, we recommend that you seek medical attention immediately.
Complications of gallstones
Complications from gallstones can be extremely painful and even fatal.
The most frequent are:
1. Cholecystitis (acute and chronic)
Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder.
It occurs suddenly due to gallstone obstruction in the bile ducts and can be acute or chronic.
- Symptoms:
Severe abdominal pain in the upper right part, fever, nausea and vomiting.
- Complications:
If left untreated, acute cholecystitis can lead to gallbladder abscess formation or even gallbladder perforation.
Chronic cholecystitis can cause irreversible damage to the gallbladder.
- Treatment:
Treatment can range from changes in diet to surgery to remove the gallbladder (cholecystectomy).
2. Cholelithiasis or gallstones
They are solid deposits that form in the gallbladder or bile ducts.
- Symptoms:
Severe abdominal pain, especially after a high-fat meal.
- Complications:
Gallstones can block the bile ducts, causing inflammation and infection in the gallbladder and ducts, and triggering other complications.
- Treatment:
Gallbladder removal surgery, known as cholecystectomy, is the main treatment.
3. Choledocholithiasis
Choledocholithiasis is the presence of gallstones in the common bile duct, the duct that carries bile from the gallbladder to the small intestine.
- Symptoms:
Abdominal pain, jaundice, fever and symptoms of biliary obstruction.
- Complications:
Pancreatitis, liver abscess and obstruction of the common bile duct.
- Treatment:
Stone removal is often performed using endoscopic procedures, such as endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP).
4. Acute lithiasis pancreatitis due to gallstones
It is an inflammation of the pancreas caused by the migration of gallstones into the pancreatic ducts.
- Symptoms:
Severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, jaundice in some cases.
- Complications:
Acute pancreatitis can be life-threatening and require intensive care.
- Treatment:
It may include hospitalization, symptom management, gallstone removal, and treatment of complications.
Can gallstones be prevented?
While it is not always possible to prevent the formation of gallstones, there are certain risk factors and habits that can influence their development.
Here are some recommendations to reduce the risk of gallstones:
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce the risk of gallstones associated with being overweight and obese.
- Eat a diet rich in fiber and low in saturated fat and cholesterol.
- Moderate alcohol consumption. Alcohol can interfere with the normal function of the gallbladder and bile ducts and can increase the concentration of cholesterol in the bile.
- Drink enough water to keep the bile diluted.
- Avoid rapid weight loss and extremely low-calorie diets, as the liver releases more cholesterol into the bile, which can contribute to the formation of cholesterol stones.
- Keep chronic diseases like diabetes under control.
Cholelithiasis is a condition that can significantly affect your quality of life and, in some cases, lead to serious complications.
So, if you suspect gallstones, see your GP immediately for referral to a specialist or speak directly to our expert surgeons.
Treatment for cholelithiasis here >>
We are here to help you!