Epidermoid cyst
Among the most frequent pathologies treated, the epidermoid cyst manifests as a lump under the skin.
Epidermoid cyst
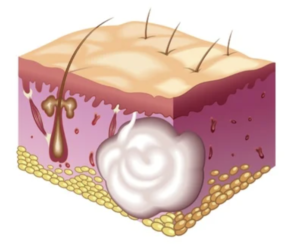
An epidermoid cyst (also misnamed sebaceous cyst) is a benign cyst that originates in the skin. They are usually produced by the obstruction of the duct of a sebaceous gland associated with a hair follicle.
They are usually rounded, firm, asymptomatic, slow-growing lesions, located mainly on the trunk, neck, face, scrotum or behind the ears. Occasionally they may exude macerated keratin, with a very characteristic rancid odor, through a pore.
They are prone to infection and may form painful abscesses that require urgent surgical drainage. For this reason, their removal is recommended when they acquire a significant size.
Frequently Asked Questions
about Pilonidal Sinus
- Reddening of the skin
- Pain
- Presence of pus or blood in an opening of the skin.
- Unpleasant odor of oozing pus.
This pathology should be treated by a specialist in coloproctology, which is responsible for the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the colon, rectum and anus.
As we know, the pilonidal cyst is located in the region above the intergluteal fold, an area of treatment for this specialist.



